Analysis of the 2021 proposed Health budget
)
- President Muhammadu Buhari presented the Federal Government 2021 proposed budget before a joint sitting of the National Assembly on 8 October 2020.
The Federal Government plans to spend N13.08 trillion in 2021, which is 21% higher than the 2020 revised budget. The increase is mainly due to the addition of 50 Government Owned Enterprises and Agencies (GOEs) that were not included in the 2020 budget.
The Federal Government budget, excluding GOEs and project tied loans, increased from N9.97 trillion in 2020 to N11.02 trillion in 2021, an increase of 10.5%. Table 1 below summarizes the proposed changes in the main expenditure lines in the 2021 budget.
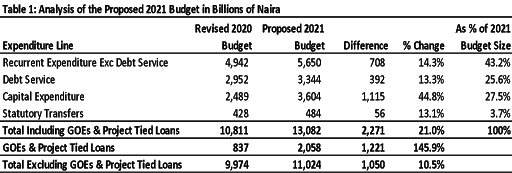
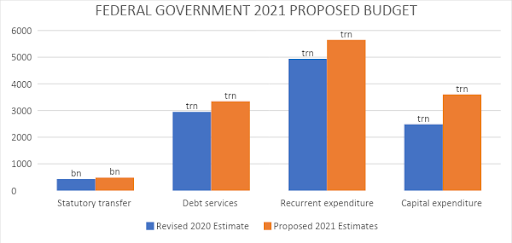
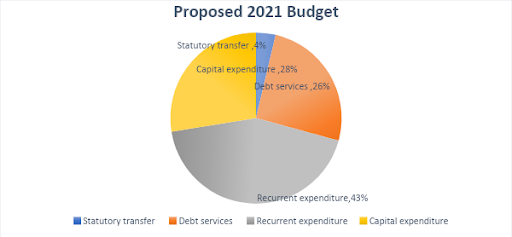
- Recurrent expenditure, excluding debt service, constitutes 43.2% of the budget, while capital expenditure accounts for 27.5% of the budget. Meanwhile, debt service was allocated 25.6% of the budget, while statutory transfers will account for 3.7% of expenditure.
- The N13.08 trillion budget will be financed by N7.53 trillion of Federal Government revenue, N1.27 trillion project tied loans/asset sales and N4.28 trillion in new domestic and foreign debt. The biggest challenge facing the Federal Government is low capacity to generate revenue, with new debt required to fund 32.7% of the 2021 budget. The revenue constraints imply the Federal Government is unable to increase capital spending, as estimated revenue cannot cover recurrent expenditure. Consequently, all capital expenditure is debt financed.
PROPOSED 2021 HEALTH BUDGET
The sum of N414.5 billion was allocated to health in the 2020 revised Federal budget (excluding covid-19 health related expenditure), while the sum of N547 billion was allocated to health in the 2021 budget, an increase of 32%. This compares favorably to the 21% increase in the overall Federal budget. Table 2 provides further details.
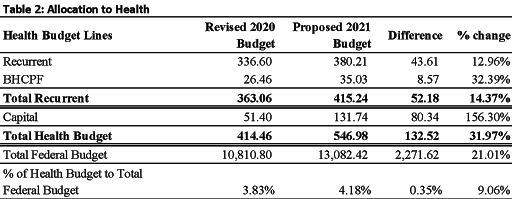
The 2021 proposed health budget is 4.18% of the total Federal budget an increase compared to 3.83% in the revised 2020 budget. However, this is still significantly below the 15% recommended in the National Health Act, 2014 and the 2001 Abuja Declaration.
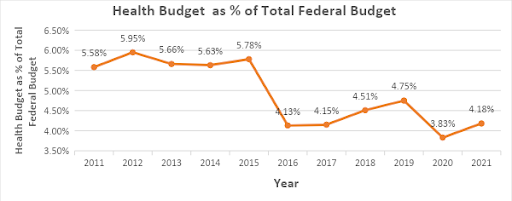
The trend of allocation to health budget as a proportion of the total Federal budget has been downward as shown in figure 3. For example, the allocation to health dropped from 5.95% of total budget size in 2012 to 4.18% in 2021. The enactment of the National Health Act in 2014 and introduction of the Basic Health Care Provision Fund in 2018, did not improve allocation to health, as a proportion of the total Federal budget. Indeed, allocation as percentage of Federal budget has dropped, with the lowest in 2020 at 3.83%.
BASIC HEALTH CARE PROVISION FUND
The Basic Health Care Provision Fund (BHCPF) was created under section 11 paragraph (2) of the National Health Act, 2014. The Fund is to be financed by at least one per cent of Federal Government Consolidated Revenue Fund. The BHCPF is meant to provide for essential drugs, vaccines and consumables; provision and maintenance of facilities, equipment and transportation in PCSs; and emergency medical treatments.
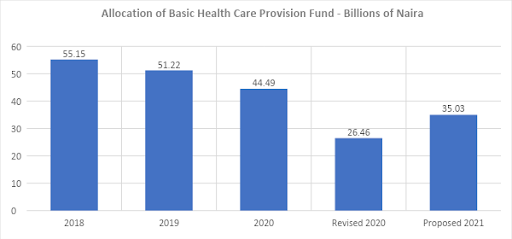
The BHCPF was finally implemented in 2018, that is four years after enactment of the National Health Act. The sum of N55.15 billion was budgeted for the Fund in 2018. The budgetary allocation to the Fund has been on a downward trend, consistent with the downward trend in Federal revenue projections, with N35 billion budgeted for the Fund in the 2021 proposed budget. Figure 4 provides further details of the trend.
RECURRENT AND CAPITAL EXPENDITURE IN THE HEALTH BUDGET
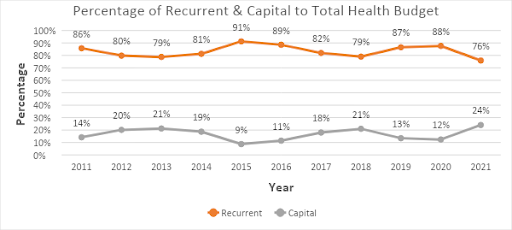
The allocation to health recurrent expenditure in the 2021 budget was N415 billion compared to N363 billion in the 2020 revised budget, an increase of 14.4%. The health capital increased from N51 billion in the 2020 revised budget to N132 billion in the proposed 2021 budget, an increase of 156%.
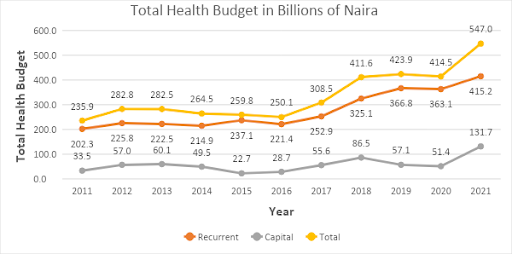
The increase in allocation to capital expenditure relating to health may not be unconnected with the obvious need for additional investments in health, as a result of the coronavirus pandemic.
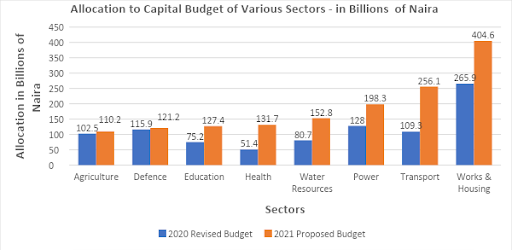
COMPARING ALLOCATION TO HEALTH CAPITAL WITH OTHER KEY SECTORS
Although allocation to health capital budget was increased in 2021 proposed budget, sectors such as Transport, Works and Housing, Water Resources and Power still received more allocation than health.
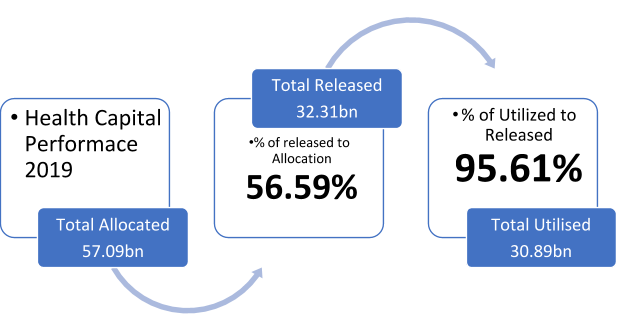
HEALTH CAPITAL PERFORMANCE
The sum of N32.31 was released in 2019 for health capital expenditure, out of which N30.89 billion was utilized as at end of 2019. The information on 2020 capital releases is yet to be published.
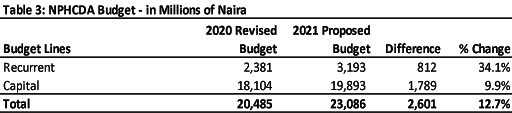
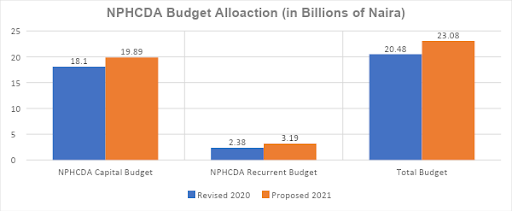
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE UNDER ONE ROOF (PHCUOR)
The proposed allocation to the capital budget of National Primary Health Care Development Agency shows an increase from N18.1 billion to N19.9 billion, representing an increase of 9.9%. The recurrent budget was also increased from N2.4 billion to N3.2 billion, an increase of 34.1%. Thus, the overall budget increased from N20.5 billion in the revised 2020 to N23.1 billion in the proposed 2021 budget, representing an increase of 12.7%.
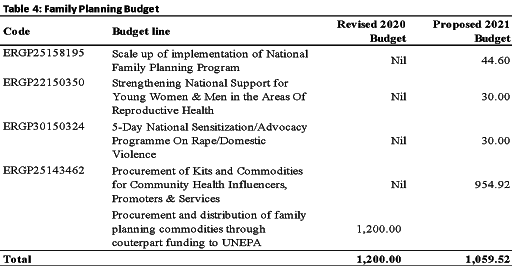
FAMILY PLANNING
Family Planning was broken down into four budget lines in the 2021 proposed budget compared to one in 2020 revised budget. However, the N1.06 billion allocation to Family Planning (FP) in the proposed 2021 budget is less than the N1.2 billion allocated in the revised 2020 budget. Funding is yet to be released for procurement of FP commodities in 2020.
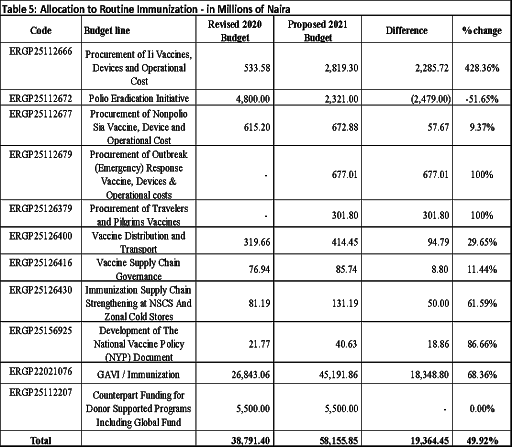
ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION (RI)
Allocation for routine immunization increased significantly from N38.8 billion to N58.2 billion in the proposed 2021 budget, an increase of 50%, signifying increasing commitment by government to immunization.
CHILDHOOD KILLER DISEASES (CKD)
Under CKD, there was no allocation in the 2021 proposed budget for IMNCH Strategy - Articulation of Policy and Strategy in Child Health in Line with SDG Targets on Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (IMCI), Integrated Supportive Supervision (ISS) and Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC). Total allocation to CKD increased from N395.8 million in 2020 revised budget to N1.15 billion in the proposed 2021 budget.

KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The total Federal Government budget size was increased from N10.81 trillion in 2020 to N13.08 trillion in 2021, an increase of 21%.
- The total Health budget increased from N414.5 billion to N546 billion, that is an increase of 32%.
- The percentage of health budget to total Federal budget increased from 3.83% in 2020 to 4.18% in the 2021 budget, which is lower than the 15% recommended in the National Health Act, 2014.
- The Basic Health Care Provision Fund (BHCPF) increased from N26 billion to N35 billion, in line with Federal Government revenue projections.
- The allocation to health recurrent expenditure increased from N363 billion in 2020 to N415 billion in the 2021, an increase of 14.4%.
- The health capital budget increased to N132 billion, an increase of N80 billion compared to the allocation in the 2020 revised budget.
- The allocation to NPHCDA increased from N20.5 billion to N23.09 billion, while the FP budget declined from N1.2 billion in the 2020 budget to N1.06 billion in the 2021 budget.
- The RI budget increased from N38.8 billion in the 2020 budget to N58.2 billion in the 2021 budget.
The budget for Child Killer Diseases increased from N395.8 million in 2020 to N1.15 billion in the 2021 budget.
)
![Aisha blows hot on Security forces; Y7ou won't believe what she said [VIDEO]](https://image.api.sportal365.com/process/smp-images-production/pulse.ng/17082024/1f976edf-1ee2-4644-8ba1-7b52359e1a8f?operations=autocrop(640:427))
)
)
)
![Lagos state Governor, Babajide Sanwo-Olu visited the Infectious Disease Hospital in Yaba where the Coronavirus index patient is being managed. [Twitter/@jidesanwoolu]](https://image.api.sportal365.com/process/smp-images-production/pulse.ng/16082024/377b73a6-190e-4c77-b687-ca4cb1ee7489?operations=autocrop(236:157))
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)